As 2013 begins, all seventeen Beacon Community initiatives are finishing up their pilot programs. In the coming months, these communities will be reporting on their results.
For my blog, I’ve focused in on one Beacon Community to share their story and insights about using technology to engage patients through two successful remote monitoring pilots. I also wanted to share their plans for expanding capabilities to engage patients in future pilots.
Dr Alan Snell, CMIO at St Vincent Health was in on the grant writing for the Central Indiana Beacon Community back in early 2010. HHS Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT (ONC) awarded their Beacon Community over $16 million for several projects including remote home monitoring.
December 2010, Dr Snell and his team launched their first remote monitoring project designed to reduce the 30- day readmission rate for patients with a discharge diagnosis of CHF and/or COPD. January 2012, Dr Snell expanded the remote monitoring to include another pilot targeting patients with complex chronic management (i.e. 6+ chronic conditions) who were high risk and high resource utlizers.
Pilot Remote Monitoring Technologies
Patients in both remote monitoring pilots used the same tools and resources but their access to them varied. Since the first pilot was designed to keep them out of the hospital based on CMS guidelines, patients were randomized after signing consents to participate in the remote monitoring program for 30 days. As a side note, since the Central Indiana Beacon Community is connected to the Indiana Health Exchange (IHIE), they will be able to effectively evaluate whether the patient was readmitted to any of the area hospitals.
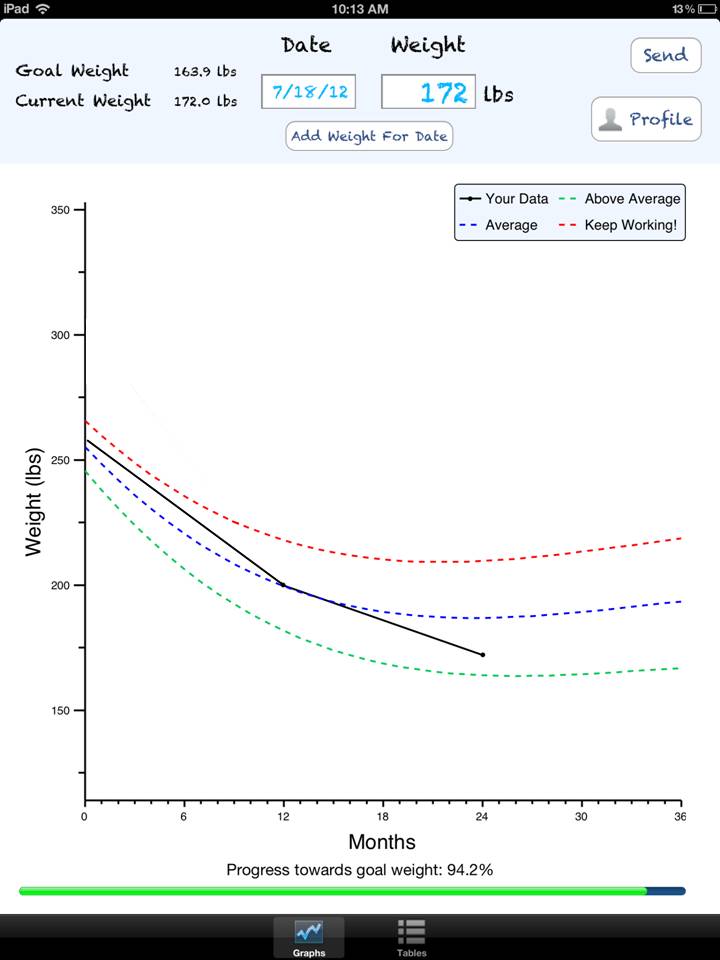
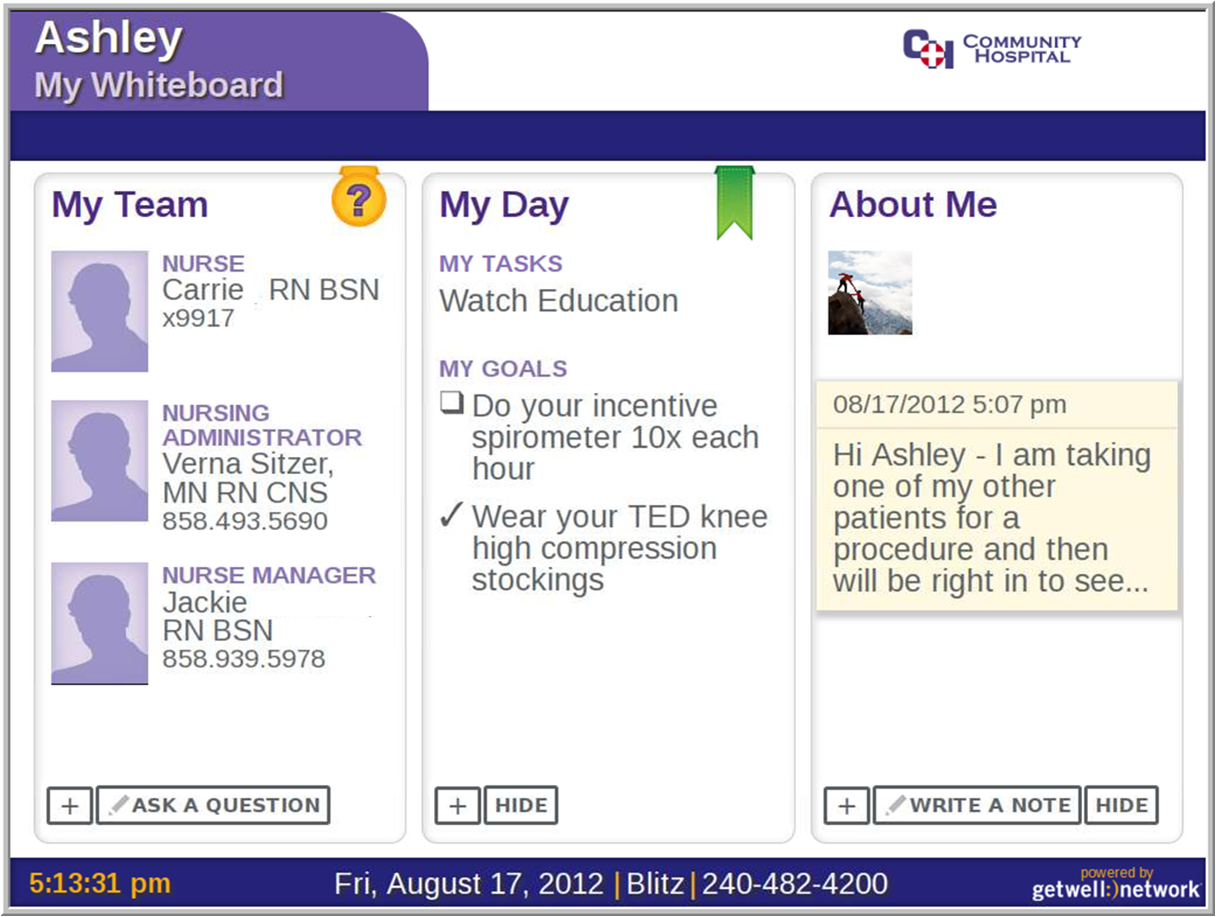
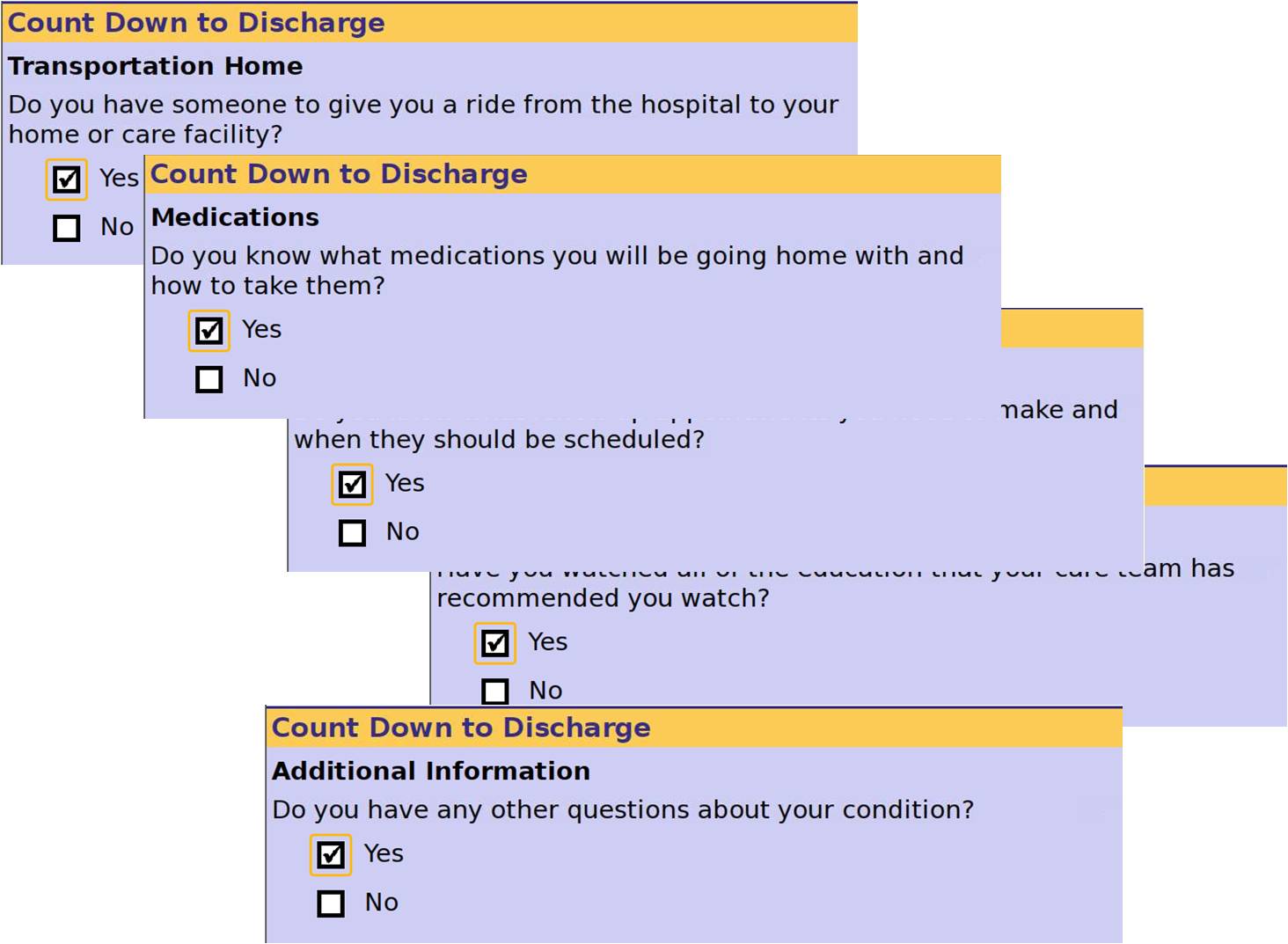
For the pilots, patients were given an electronic health guide to place in their home to help monitor and manage their health. On a daily basis, patients interacted with this small wireless mobile device to answer six questions (i.e. fatigue, pain level, shortness of breath, etc) and provide additional requested information based on their responses. Patients also measured their vitals using a Bluetooth scale and a blood pressure cuff and some were asked to use a Bluetooth pulse oximeter. Each patient participated in scheduled video conference calls with their assigned nurse to address questions and enable the nurse to see how the patient was really doing.
Pilot Insights: Patient eHealth Engagement
The Central Indiana Beacon Community chose the remote monitoring technology for their pilots back in 2010. The device they selected was essentially “first generation” and cost around $2,000 each. Today, similar devices cost around $500 each and have more functionality to support the patient with collecting their health data and communicating with their clinicians and care team.
During the remote monitoring pilots, The Central Indiana Beacon Community gained insight into how technology supported and improved patient care:
Impact of Video Conference with Nurse: The Central Indiana Beacon Community utilized a wireless device that delivered 3G video conferencing capabilities. “We were interested in testing more than just the conferencing technology in our pilot. We wanted to determine whether the technology enabled the nurse to create a personal connection with the patient and motivate them for better outcomes”, explains Dr Snell.
“The video conferencing capability helped our nurses build a trusted relationship with the patient”, adds Julia Smalley, MBA, RN, Director, Innovations Accelerator Team at Ascension Health Alliance. “During the video conference session, our nurse did a visual assessment and was to ask further questions to uncover why the patient didn’t look right. When the patient appeared confused, the nurse provided a more detailed explanation. We’ve noticed that this personal connection leads to a better relationship which means better compliance since the patient feels more compelled to do what is right”.
Value of Patient Experience Information: The remote monitoring guide gathered information from the patient (e.g. six daily questions) about how they were feeling to both capture trending information as well as determine if an early intervention was needed. “We’ve found that collecting self reported experience data on a daily basis alerted us to respond faster than if we waited for problems to appear in their vitals”, emphasized Dr Snell.
“We set up a flag to alert us when we received certain answers from the patient. This way we were able to reach out immediately before there was a further decline”, adds Smalley. She further stressed the strong value of using the patient’s experience information as a “teachable moment” to help the patient understand his trigger points and explain why he was feeling that way.
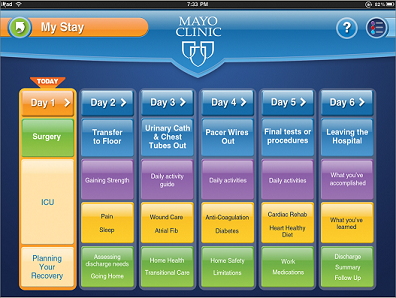
Value of Patient Education Tools: Within the wireless guide, patients were able to view any of the seventeen imbedded videos to learn about how to better care for their chronic conditions, the importance of proper diet and exercise, when to contact their provider, etc. “Our nurses also directed the patient to a specific video when she saw out of range biometrics, concerning answers to the health questions or an education need during the scheduled video conferences,” shares Smalley.
Future: Patient & Family eHealth Engagement
The Central Indiana Beacon Community pilot has ended. However, St. Vincent Health and Ascension Health Alliance have formed a joint venture and are incorporating the pilot learnings into development of a Remote Care Management Program.
“Although extensive analysis is underway, we are already planning our remote monitoring initiatives which will focus on the same two patient populations from the pilots (e.g. 30- day discharge, complex chronic patients). We are investing in a new care management platform which will enable us to capture and share patient monitoring information. Patients, their families and Providers will be able to log into a portal to view vital sign measurements, care plan compliance and communicate with the care team about any concerns,” explains Dr. Snell.
Since patient education is so important, the platform supporting the new Remote Care Management Program will have more content and capabilities including the ability for the patient to take teach back quizzes as well as notes to share with care givers. Physicians will be able to monitor their patient’s education and quiz results since it will be placed in the electronic medical record. This will guide the physician to have better conversations with their patients and provide needed support.
During the pilot, the care team heard about the patient’s interest in getting their family members involved to support their daily lifestyle decisions such as helping them read food labels and understand how diet impacts their health.
“We will be able to use our portal and mobile technologies to provide ongoing education to patients and their families and provide access to a skilled clinicians 24x7, which will significantly extend access beyond our pilot”, adds Dr Snell.
“As we think about using mobile in future pilots, we are considering the ability of our patients to use technology. Some of our younger and tech savvy patients will be able to use a smart phone to record their measures and access educational content while our older patients will feel more comfortable using a mobile tablet to watch videos and respond to questions”, explains Smalley.
Dr Snell and his team are using the pilot insights to define their care management platform requirements to support the Remote Monitoring Program. Based on what I’ve learned about their technology direction, they are incorporating three key engagement elements into the design of their platform. First, they are providing the patient with the tool set and skills to help them self manage with ongoing reinforcement from the care team. Second, they are developing a solution with integrated tools and information to support “connected health”. Their remote monitoring data will be connected into a care management platform to share information with across the care team and family members, which supports meaningful use. Third, they are planning to incorporate technologies to meet the needs of their different patient segments and are carefully considering how each will use the online and mobile capabilities. This will be an important engagement driver since patients need to feel comfortable using technology to collect their health data, and collaborate with their care givers on their personalized care plan.
 Motivation for health and wellness,
Motivation for health and wellness,  care collaboration,
care collaboration,  consumer generated health and wellness content,
consumer generated health and wellness content,  educating consumers about health and wellness,
educating consumers about health and wellness,  mobile health application,
mobile health application,  patient education,
patient education,  patient ehealth engagement,
patient ehealth engagement,  personalization for health and wellness,
personalization for health and wellness,  self- management health tools in
self- management health tools in  Behavior Change Health & Wellness,
Behavior Change Health & Wellness,  Connected Health,
Connected Health,  Data Driven Health Engagement,
Data Driven Health Engagement,  Decision Support eHealth,
Decision Support eHealth,  Mobile Engagement Health & Wellness,
Mobile Engagement Health & Wellness,  Patient Engagement,
Patient Engagement,  Personalization eHealth
Personalization eHealth